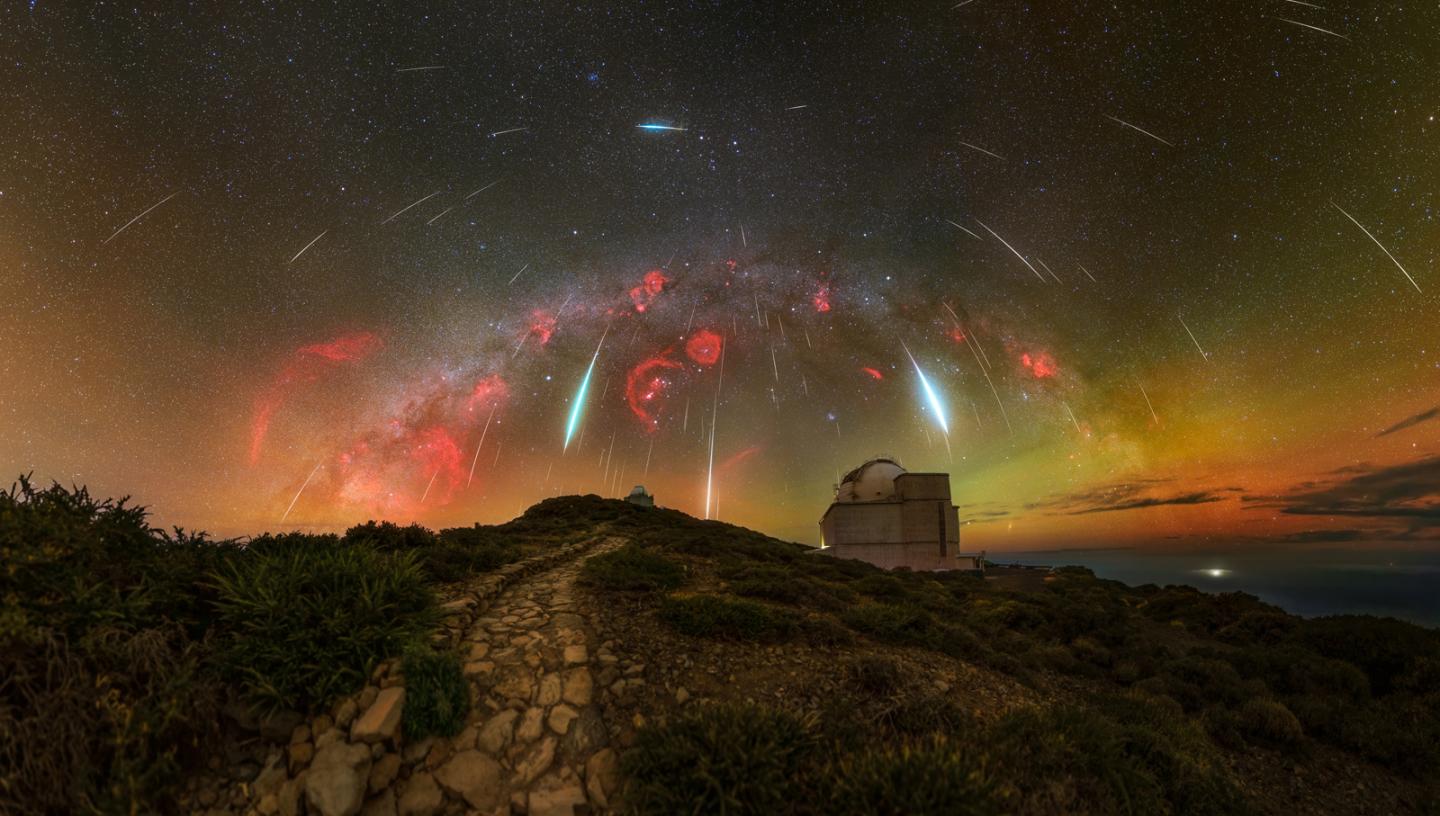
The Geminid meteor shower is one of the last of the year’s major showers, and can generally be relied on to put on a good display.
In 2025, the Geminid meteor shower will be active between 4-20 December and will peak on 14 December.
What is the Geminid meteor shower?
Meteors are pieces of debris which enter our planet’s atmosphere at speeds of up to 70 kilometres per second, vaporising and causing the streaks of light we call meteors.
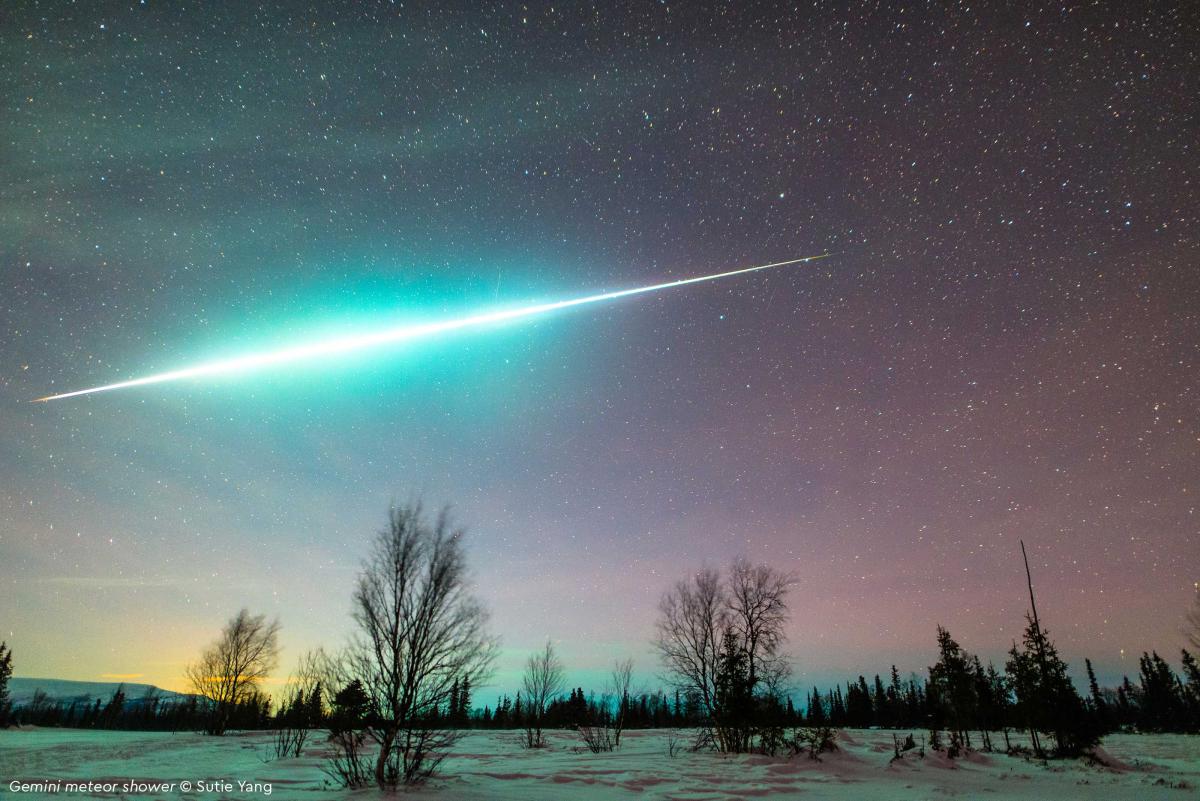

The meteors of the Geminid meteor shower are very bright, moderately fast, and are unusual in being multi-coloured – mainly white, some yellow and a few green, red and blue. These colours are partly caused by the presence of traces of metals like sodium and calcium, the same effect that is used to make fireworks colourful.
The shower has been known to produce over 120 meteors per hour at its peak, although light pollution and other factors mean that in reality the actual number visible is far less.
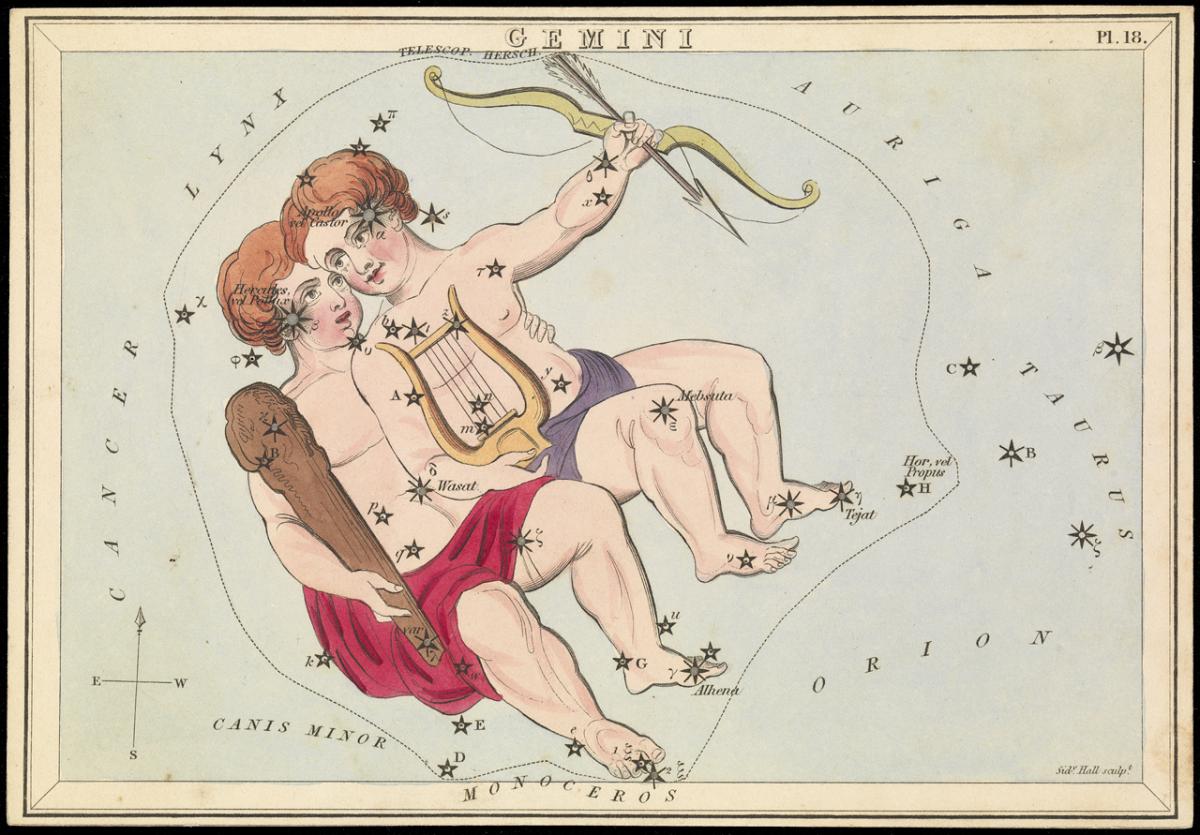
Geminid meteors appear to radiate from near the bright star Castor in the constellation of Gemini.
What sets the Geminids apart from other meteor showers is their origin: while most meteor showers originate from comets, Geminids are leftover bits and pieces of the asteroid known as 3200 Phaethon. Unlike comets, asteroids don’t develop tails when approaching the Sun, and their composition is different.
However, scientists are still debating if Phaethon is even an asteroid - although it is built like one, it doesn’t move like one. Its orbit is highly elliptical, like a comet, which is why some scientists debate if Phaethon could be a completely new class of celestial objects: a rock comet.
When is the Geminid meteor shower in 2025?
| SHOWER NAME | DATE OF MAXIMUM | NORMAL LIMITS | PEAK RATE/HOUR | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geminids | 14 December | 4-20 December | 120 | Plenty of bright meteors, few trains |
Find more meteor showers this year
Geminid meteor shower facts
- The Quadrantids and the Geminids are the only major meteor showers which don't originate from a comet.
- The beautiful streaks we see in the night sky can actually be caused by particles as small as a grain of sand!
- The Geminids were first observed in 1862, much more recently than other showers such as the Perseids and Leonids.
- The Geminids are thought to be intensifying every year.
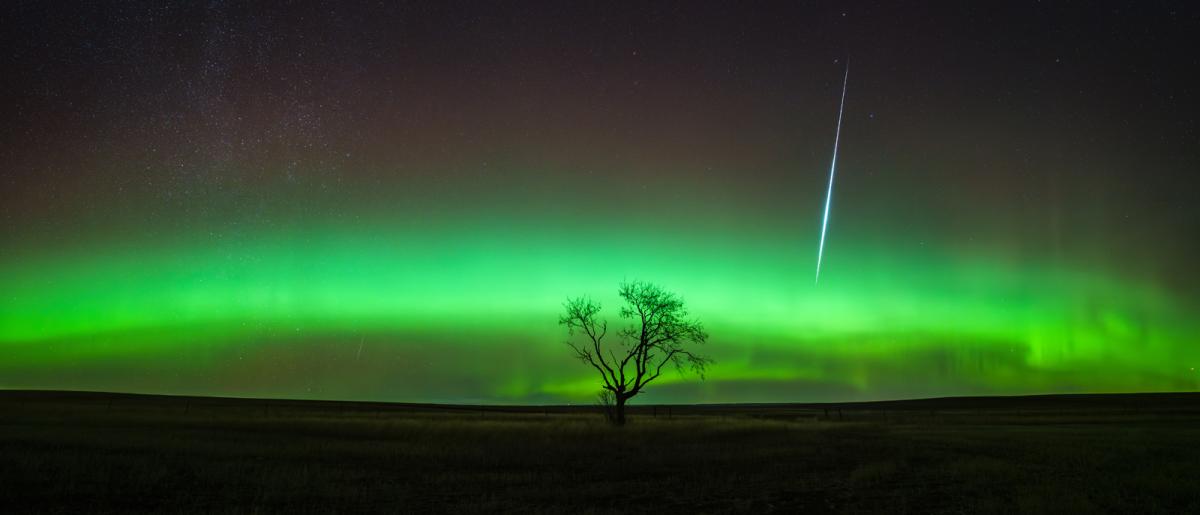

How can I watch the Geminid meteor shower?
The Geminid meteor shower is one of the most active showers of the year, and in some years is the strongest, with a peak rate of up to 120 meteors per hour. It is the one major shower that shows good activity before midnight.
In 2025 the maximum will occur on 14 December when the Moon is a waning crescent, so viewing conditions are reasonably favourable.
Hunting for meteors, like the rest of astronomy, is a waiting game, so it's best to bring a comfy chair to sit on and to wrap up warm as you could be outside for a while. They can be seen with the naked eye so there's no need for binoculars or a telescope, though you will need to allow your eyes to adjust to the dark.
It is best not to look directly at the radiant as this can limit the number of meteors you see. Try instead to look just to the side in a dark area of sky and you will be more likely to catch sight of some meteors.
Where is best to watch the Geminid meteor shower?
For the best conditions, you want to find a safe location away from street lights and other sources of light pollution. The meteors can be seen in all parts of the sky, so it’s ideal to go to a wide open space where you can scan the night sky with your eyes. But if you trace the paths that the meteors take, they seem to originate from the Gemini constellation.
If you manage to get any pictures of the Geminid meteor shower then we'd love to see them. You can find us on Facebook or Twitter.
What is the difference between an asteroid, a meteoroid, a meteorite and a comet?
Read more about comets, meteors and asteroids.

Meteor shower calendar
Header image: A Cosmic Firework: the Geminid Meteor Shower © Jakob Sahner, shortlisted in Astronomy Photographer of the Year 2024


