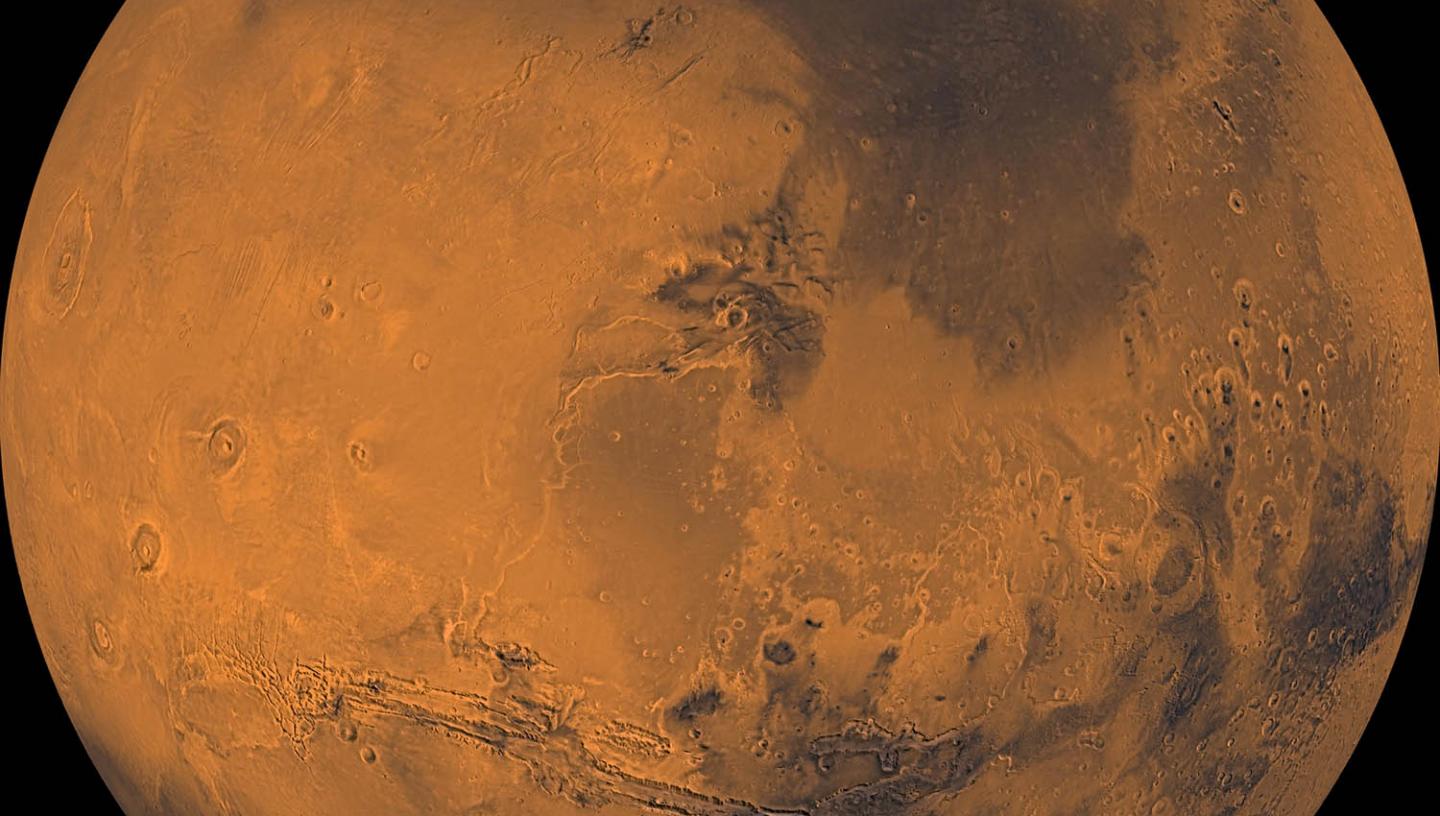
No other planet has been studied as closely as Mars, barring our own planet Earth of course. But what do we know about the Red Planet? And could humans ever live there?
Planet Mars facts
Size: 6794 km in diameter
Distance from Sun: 228 million km (142 million miles) on average
Average Temperature: Around -65°C (-85°F)
What does Mars look like - and can you see it from the Earth?
From the Earth, Mars is easily seen in the night sky as a red point of light. It slowly drifts against the background stars, changing the constellation it can be found in from month to month and taking around two years to return to the same part of the sky.
Seen through a telescope Mars appears as a small reddish disk on whose surface dark markings can (with difficulty) be seen. One of its polar caps may also be visible.
However, even with large telescopes it is very difficult to see detail, and many experienced observers were deceived into thinking that they had glimpsed features, such as the infamous canals, that in fact were not there.
Almost all that we know about the surface of Mars and its atmosphere has been discovered by the various space probes that have orbited the planet and landed on its surface.
Why is Mars red?
Mars is frequently referred to as the Red Planet. Its unique colour is due to iron minerals in the Martian surface. The iron oxidises or rusts, causing the planet to appear red.
What is the atmosphere of Mars?
We know that the atmosphere of Mars has a pressure less than one hundredth of the Earth's, and that it is composed mainly of carbon dioxide with a little nitrogen and argon. There is almost no oxygen.
This very thin atmosphere traps very little heat meaning that the mild greenhouse effect that keeps the Earth slightly warmer than its distance from the Sun would imply is almost non-existent on Mars.
Is there water on Mars?
There is a small amount of water vapour which condenses in some places to produce thin clouds and fog. There are also polar caps at each pole which grow in the Martian winters with the addition of deposits of solid carbon dioxide, and decrease in the Martian summers to leave what is thought to be a small residue of ordinary water ice.
The surface of Mars shows impact craters, like the Moon, mountains, rift valleys, ridges, hills plains and extinct volcanoes. Some of these features, like deep craters, protect permafrost trapped in the coldest parts of the surface.
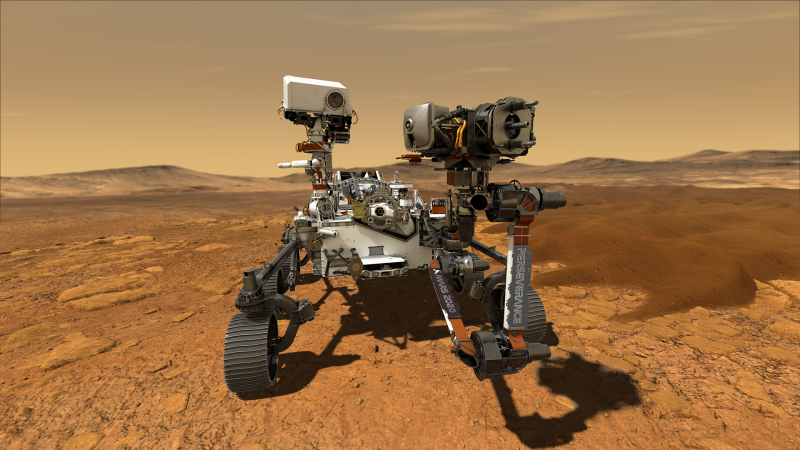
In the past few decades, robotic rovers on Mars like NASA's Curiosity and Perseverance rovers have found evidence that Mars once had large quantities of liquid water that stayed on the surface as rivers, lakes, even possibly oceans. However, some climate disaster, most likely in part due to Mars' small size, eventually led to the stripping of its atmosphere and the loss of most of the water protected beneath. What remains today is likely a fraction of what water Mars once had, though the possibility of sizeable stores. However, there are signs that some of this water may be trapped in mineral deposits underground, with NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter uncovering what could be underground lakes, though quite how much water they contain is hard to determine.
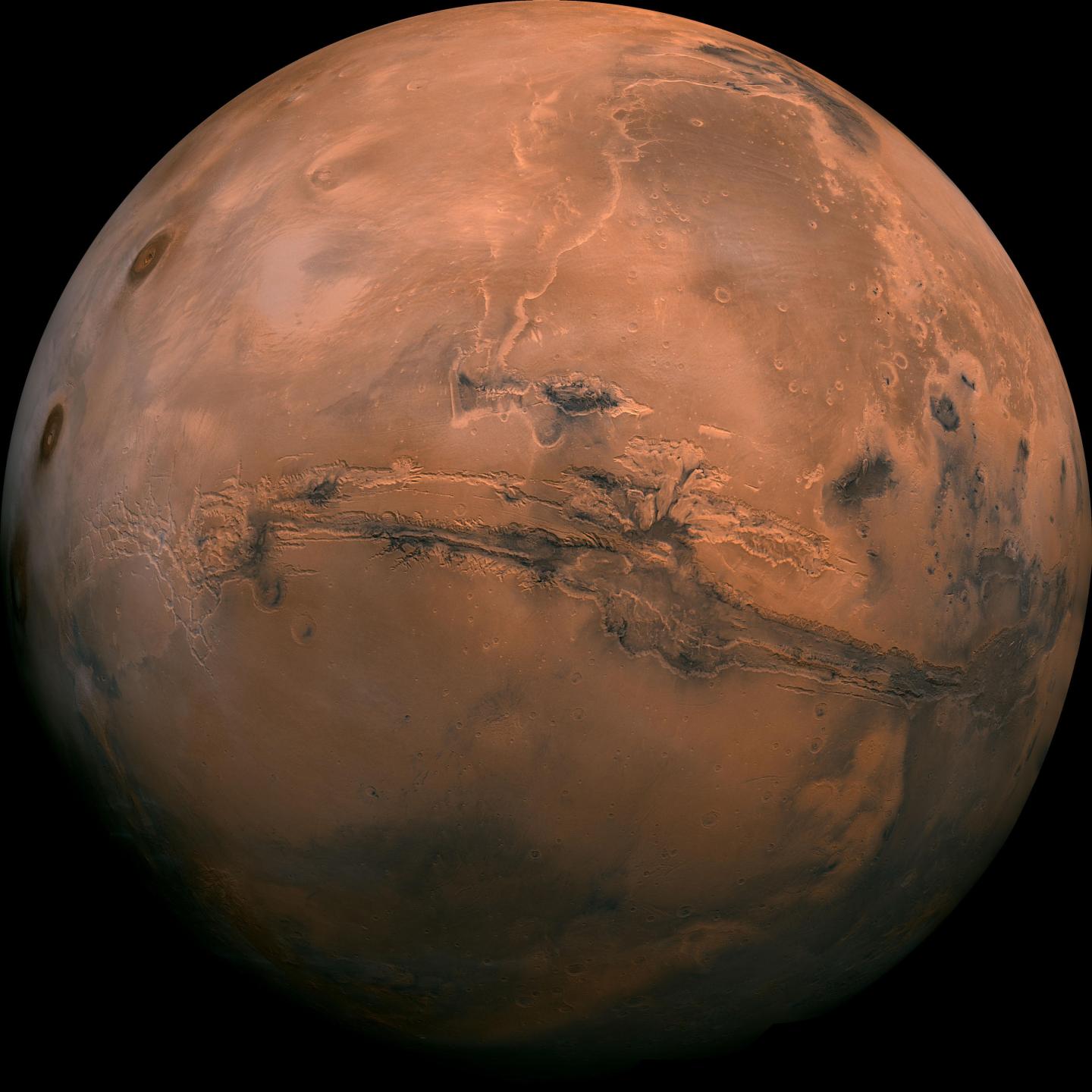
What is the temperature on Mars?
The surface temperatures on Mars can occasionally rise to about 20°C in the hottest places in summer months but regularly fall to near -100°C before sunrise. With an average temperature of -65°C, Mars is far from the habitable planet our own Earth is.
Despite the thin atmosphere, winds can also be surprisingly strong and are responsible for extensive weathering of the rocks on the surface. Sometimes these winds blow up enormous sandstorms that can obscure the view of the planet's surface. One such event caused the end of NASA's Opportunity rover when its solar powered batteries ran out of charge as a dense sandstorm dropped light levels for many weeks.
How long is a day on Mars?
The planet Mars rotates in 24 hours and 37 minutes about an axis tilted by 24° to its orbital plane. That makes a day on Mars only slightly longer than a day on Earth. However, a year on Mars is much longer than a year on Earth lasting 687 Earth days or a little under two years.
Learn more about a day on Mars
How many moons does Mars have?
The planet Mars has two moons, Phobos and Deimos. They are both very small, being less than 30 km across. While it was once thought that they might be captured asteroids from the asteroid belt, it is now generally thought that they are the product of a huge collision between Mars and a large asteroid or planetesimal, similar to how our own Moon was formed.
Phobos is very close to Mars and its orbital period (8 hours) is less than the rotational period of Mars meaning it would actually overtake an observer on the ground, being seen to rise in the west and set in the east. Deimos is further away from Mars and would be seen to behave more conventionally.
How long would it take to get to Mars?
On average Mars is 225 million km (140 million miles) from Earth, although that distance is constantly changing as both the Earth and Mars orbit the Sun.
The moment of 'closest approach' is when Mars and Earth come nearest to each other during their orbits. At these times, Mars is only 60 million kilometres (37 million miles) away, though the exact distance depends on the exact orbits of each planet. The next Mars closest approach will be on 8 December 2022, with another following around two years later on 16 January 2025.
The time it takes to get to Mars from Earth depends upon where each planet is in the Solar System and what the spacecraft aims to do when it gets there. If a flyby of the planet is all that is needed, perhaps on a longer trip to the outer solar system, then a fast almost straight line to the planet is possible. However, if you intend to orbit or even land on the planet then a longer curved path taking around 7-8 months is far easier to slow down from.
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2005 for example took 210 days to reach Mars, while Mariner 9, the first spacecraft to orbit Mars, took 168 days in 1971.
Nasa's Mars 2020 mission, containing the Perseverance rover, launched on the 30th July 2020 and landed on 18 February 2021 meaning it took 203 days to reach the surface of Mars.
Sunlight, meanwhile, takes only 13 minutes to travel from the Sun to Mars and the radio signals that are used to control the rovers take between five and twenty minutes to travel from Earth to Mars depending on the relative positions of each planet.
Is there life on Mars?
NASA has stated that it does not expect to find current living organisms on Mars. However, the various missions to the Martian surface have attempted to deduce whether the planet ever could have supported life - and whether it could in the future.
The Mars Curiosity Rover has been exploring the planet since 6 August 2012, while one of the stated goals of the Mars 2020 mission is to research how the planet could sustain future human missions to Mars. This will include testing a method for producing oxygen from the Martian atmosphere.





